News: Coccydynia – pain in your tailbone
By David Cork, Osteopath
What is Coccydynia?
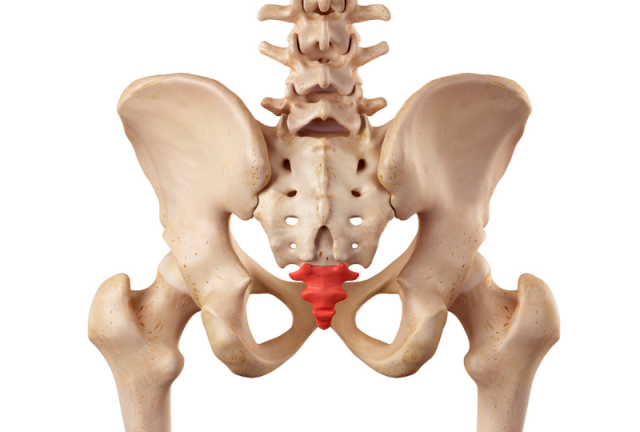
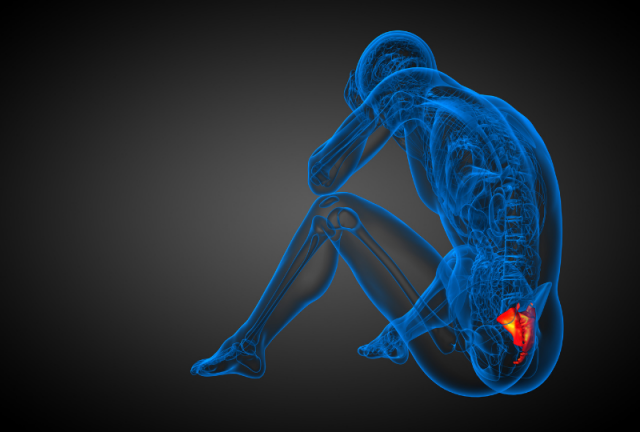
Cocccydynia is the name for pain around the coccyx or tailbone.
The coccyx makes a joint with the sacrum which moves when you go to the toilet and during childbirth. The coccyx has many attachments including pelvic floor muscles, gluteal muscles and ligaments of the pelvis.
What are the symptoms of Coccydynia?
Symptoms of Coccydynia can include:
- Tenderness, a dull ache or sharp pain at the bottom of the spine
- Pain with prolonged sitting or standing
- Pain getting up from a seated position
- Pain with sexual intercourse
- Pain with defecation, especially straining
Coccydynia can be extremely debilitating as most daily activities are done in seated or standing positions, which often aggravate the pain. It can also negatively impact basic bodily functions and personal relationships.
Common causes of Coccydynia
The most common cause is external trauma i.e. a fall onto the tailbone. Did you know women are 5 times more likely to have coccyx pain than men: the coccyx is more exposed in women (the pelvis is broader) and is put under strain during childbirth? Other causes include:
- Prolonged sitting on hard surfaces
- Haemorrhoids and excessive straining when going to the toilet
- Obesity, due to the increased load placed through the coccyx region and altered sitting positions
- Repetitive strain or friction during exercise, such as in rowing or cycling
- Compensation for other diseases related to the bowels and reproductive organs e.g. bowel Cancer
There are also a significant number of cases of Coccydynia where there is no apparent cause.
How can we help with Coccydynia?
Like most conditions, a thorough assessment is very important. There any many causes of pain in this area including referral from the low back and pain related to the bowels or reproductive organs. The great news for suffers of this condition is 90% of patients with coccyx pain will have success with conservative treatment.
If the assessment shows coccydynia is most likely the cause of the pain, the following treatments can be used:
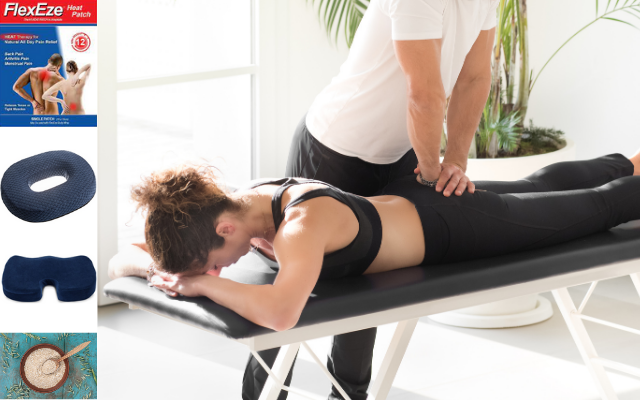
- Soft tissue massage of buttock and low back regions to reduce tension and sensitivity of muscles around the area
- Modification of physical activity
- Special cushions to reduce discomfort when sitting (e.g. a doughnut or wedge cushion)
- Home exercise program including stretching of hips and pelvis and mobility exercises of the low back
- Heat packs; anti-inflammatory medications
- Increase fibre in the diet, or use stool softeners, to help make going to the toilet easier
- Referral to pelvic floor specialist for internal techniques of the coccyx and advice on bowel function and defecation
References
- Coccydynia: An Overview of the Anatomy, Etiology, and Treatment of ..(n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3963058.
- A comparison of conservative interventions and their effectiveness ..(n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24421634.
- Coccydynia: a review of pathoanatomy, aetiology, treatment and ..(n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21119164.
- Coccydynia. (n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2682410.